Difference between revisions of "Wave mechanics"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
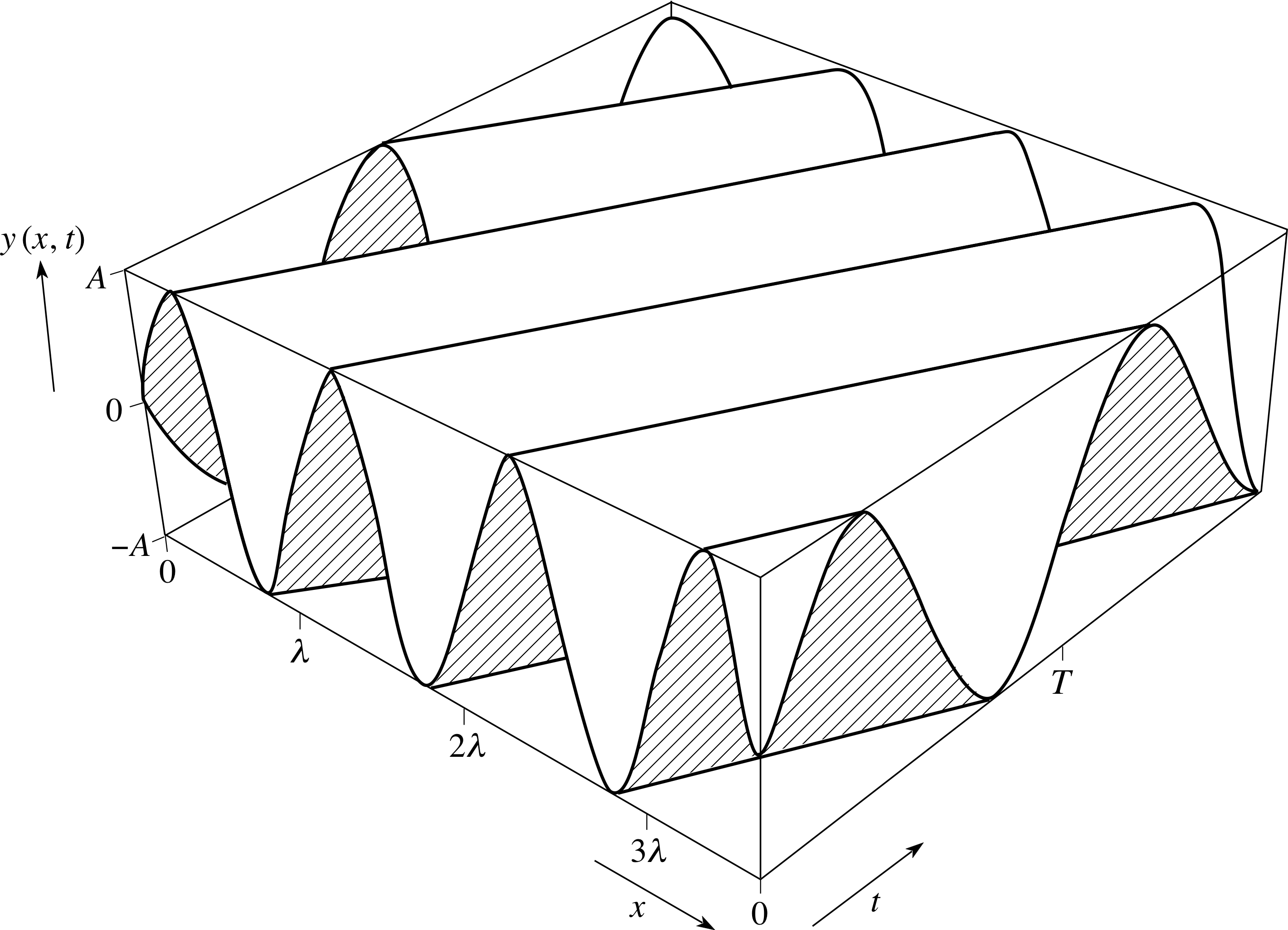
y(x,t) = Ψ = Asin(kx - ωt) | y(x,t) = Ψ = Asin(kx - ωt) | ||
| − | [file:3d plot of y and x and t.png] | + | [[file:3d plot of y and x and t.png]] |
A = amplitude | A = amplitude | ||
Revision as of 12:00, 5 May 2020
Introduction
Basic Equation
The basic equation of wave mechanics is a function that describes the position of a particle as a function of time, where the function is wavelike, such as sine or cosine:
y(x,t) = Ψ = Asin(kx - ωt)
A = amplitude
k = 2π/λ
w = 2πf
So if given the amplitude, wavelength and frequency of a particle that was behaving in a sine fashion, its position could be calculated at a particular time on the t axis using this equation. It would also give the particle position as a function of time at a particular distance on the x axis. Both plots F vs. x and F vs. t would be cosine plots.